| Bows | Napkins | Tables | Chairs | |
| Renee | 100 | 50 | 40 | 20 |
| Alex | 90 | 55 | 45 | 15 |
| Ty | 95 | 45 | 20 | 40 |
| Jack | 55 | 60 | 50 | 25 |
Who has the absolute advantage in producing tables?
FEEDBACK: The person with the absolute advantage is the one who can produce the most output. In this case, Walker can produce more brushes than anyone else, so he has the absolute advantage.
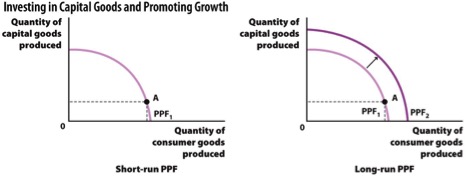
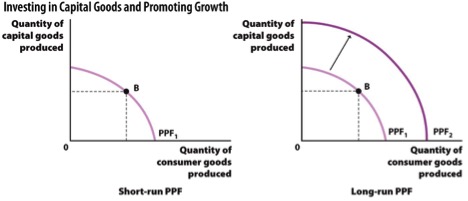
Examine the two figures below. Which of these figures will experience a higher long-run growth rate, assuming their ratio of consumer goods to capital goods produced is constant over time?
A
B
FEEDBACK: Societies that invest a relatively larger percentage of their production into capital goods, which are a type of investment in future production, experience higher growth rates. The economy in Figure A produces more consumer goods than capital goods while the economy in Figure B produces an equal proportion of consumer goods and capital goods. So, the ratio of capital to consumer goods produced is higher in economy B, and consequently economy B’s growth rate will be higher.
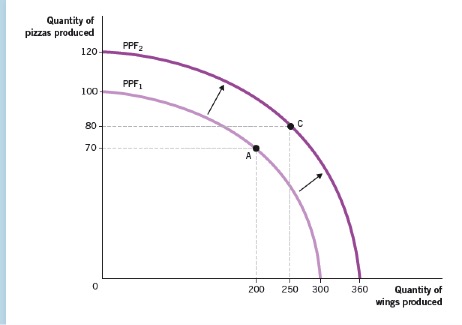
Click to view larger image.
Which of the following would lead to the situation shown in the figure above?
FEEDBACK: With improvement in technology it is possible to produce more of both goods while using the same amount of labor. This will allow the PPF to expand outward. An earthquake would destroy resources and cause the PPF to shrink inward. A reduction in retirement age would lower the size of the labor force, lower production, and cause the PPF to shrink inward. A reduction in worker skills would decrease the human capital available, decreasing production for workers and causing the PPF to shrink inward.
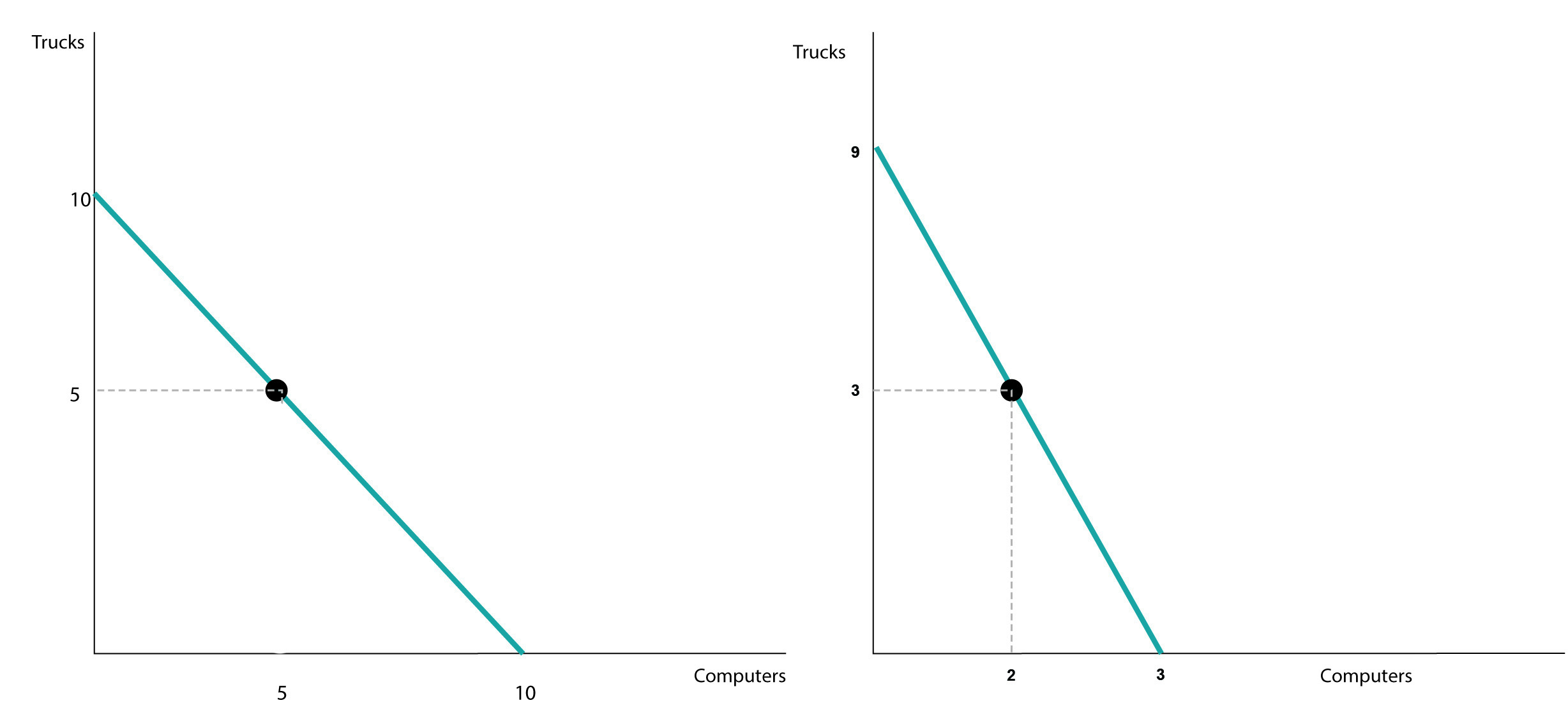
Click to view larger image.
Mike’s PPF is on the left and Debra is on the right. Therefore which of the following statements is true?
FEEDBACK: Mike has an absolute advantage in both goods. That means he can produce more than Debra using the same quantity of resources. From the graph, you can see that Mike has a lower opportunity cost in producing trucks; he gives up one truck for each computer he produces, while Debra gives up three trucks for each computer she produces. Mike has a comparative advantage in producing computers but not in producing trucks.
FEEDBACK: If the resources are already being efficiently used in other programs (and the politician cannot raise the funds from another source), then it will be impossible to build additional facilities given the existing technology and resources available. The politician could build more wind and solar power facilities, but not without decreasing production of one or more of the goods currently in production. Producing more wind and solar power facilities without decreasing current production requires more resources or technology, represented by a point outside of the current PPF.
FEEBACK: If workers become more skilled they can produce more goods. An increase in skills is an increase in human capital, a resource and input in the production of goods. When resources increase, the entire PPF shifts out.
FEEDBACK: Endogenous factors are things you can plan for and take into consideration before going to a college, such as the location and price of tuition. Exogenous factors cannot be accounted for before you begin your education at a particular college because they are not related to the college you choose.
FEEDBACK: Unemployment is represented by points inside the frontier where resources are not being used efficiently. All points on the PPF are points at which the economy is at the full-employment level of employment.
FEEDBACK: Full employment is a characteristic of all points on the production possibilities frontier. For all points on the PPF, all resources available are being used efficiently.
FEEDBACK: In economics it is important to avoid letting personal beliefs and values influence the outcome of analysis. To be as objective as possible, scientists will use positive statements, which can be tested and validated. The statement about average rainfall is something that can be validated. All other statements are normative, which have embedded value judgements.
FEEDBACK: The person with the comparative advantage is always the one with the lowest opportunity cost. This means Jonathan has a comparative advantage in producing apples if he gives up less production of other goods when he produces apples.
FEEDBACK: In the short run, the individual is valuing the present over the future. Purchasing a leather jacket instead of saving for retirement is valuing future consumption over the value of the initial savings and the return on that savings in the long run.