Contents
How to Secure Google Workspace. 4
Cloud Access Security Broker. 6
Bio-Human Google Workspace Security White Paper
Google workspace is a collaboration and communication tool meant for helping workers organize themselves and their teams and share data. Google workspace allows workers to communicate and collaborate using personal devices such as computers, smartphones, and tablets. However, the many devices and varying locations of the workers expose the workspace to malicious actors interested in stealing company secrets or personal information they can use for cash.
Google workspace has tools such as chat, Meet, Gmail, voice calling, Docs, Tasks, and video calling (Soltero, 2020). Such tools help workers in organizations of different sizes collaborate on their work, increasing efficiency at work. Today’s working environment is hybrid, with some workers preferring to work from home while others work at the office. Organizations are also employing remote workers who sometimes work from different countries. Such trends show the changes in the work environment, and Google workspace aims to help the workers work together irrespective of distance and time.
Workspace is hosted in the cloud, making it accessible from anywhere in the world, and thus people can collaborate irrespective of geographical barriers. However, hosting the tools in the cloud poses many security challenges, as any malicious actor anywhere in the world can access the information. There is a need to protect the workspace, and thus the need to have cloud security for organizations using the tools for collaboration.
Cloud Security
Bio-Human is a health care provider whose employees are mobile as they have to serve different people in different locations. The organization must have collaboration tools to help the health care workers share patient data and provide the best care. Such collaboration requires cloud-hosted tools, making Google workspace an ideal solution for BioHuman. The company needs cloud security to protect sensitive data from being accessed by external actors who can steal or expose the information, breaking the patients’ trust in BioHuman.
Hackers can access Google’s workspace and, thus, company information using different techniques such as supply chain compromise, phishing, or exploiting the public-facing applications that BioHuman employees use to access the workspace (Yang, 2020). Such methods use weaknesses in the system, such as weak user account passwords and authentication mechanisms or lack of security between applications or computer systems, whereby an attacker gains access to one application or user account and uses it to have more access to other parts or the entire system. The approach requires a firm security policy for BioHuman to protect the users and an attack on the entire IT system through a least privileged user.
Bio-Human requires cloud security that protects Google workspace from internal and external users accessing its data using unauthorized methods and from one application giving access to other applications. The company needs protection for both users and computer systems.
How to Secure Google Workspace
The various security challenges that Google workspace poses to BioHuman require different approaches to security. The solution lies in making the cloud network and user access security. Approaches such as multifactor authentication, using a secure network, zero-trust security, and secure cloud access are the best way to protect organizations such as BioHuman using Google workspace.
Secure Cloud Access
Google workspace is a cloud solution, and thus users access the collaboration tools stored in the cloud. All the information is stored and altered in the cloud. Bio-Human needs secure access to the cloud to access the workspace tools. The health care provider needs an identity management system in the cloud that administers all the user accounts and passwords used to access the tools (Schreider, 2019). The identity management system needs to authenticate all the devices that BioHuman employees use to access workspace tools and monitor them for abnormal behavior. Monitoring the system is also essential to trace any suspicious changes to the information in the workspace or unauthorized and unrecognized devices accessing the workspace (Schreider, 2019). All workers have different shifts, and it is paramount for BioHuman to have time-based access to the workspace, allowing the employees to access the data during their shifts only and flagging off any access during non-working hours. The time-based access minimizes the chances of external and internal rouge actors using authentic devices and login credentials to access the workspace.
Multifactor Authentication
The nature of work at BioHuman makes it necessary for the employees to be mobile since most are healthcare workers who attend to patients in different healthcare locations. This makes them need to use mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets and less reliance on computers. The employees, therefore, access Google workspace on mobile devices. However, malicious actors can also use such devices to access the organization’s data, leading to loss of data or breach of privacy for patients’ data. Security of mobile devices is, therefore, critical.
Multifactor authentication reduces the occurrence of external hackers accessing BioHuman’s information. Multifactor authentication involves using more than a username and password by including a second authenticator, such as a fingerprint, facial recognition, USB key, or a specific device (Microsoft, n.d.). All Bio-Human employees using Google workspace will need a second set of authenticators, making it hard for anyone to access the workspace. External attackers trying to access the healthcare provider’s data face the challenge of hacking the username/password combination. If successful, they must provide the second authenticator, which requires access to physical devices such as the user or their electronic device. The method ensures that only BioHuman employees access the Google workplace.
Cloud Access Security Broker
Cloud access best authenticates the user using the username-password value and additional security such as multifactor authentication. However, users can still have the correct credentials but access the system using devices with unencrypted channels or have malware. However, this poses a danger to companies such as BioHuman, which must comply with HIPAA policies. To comply with government regulations and have an additional layer of security, BioHuman can use Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB), which ensures organizations meet all access policies. CASB is a point in a cloud network where all policies are met for users to access cloud resources such as Google workspace, which is sensitive (Netscope, n.d.). The policies are necessary to protect the data from loss, comply with regulations, and offer visibility to the users using the workspace tools. It ensures all BioHuman employees access only the required information according to their work, and any changes in the data accessed are noted to protect the organization from data loss.
Zero Trust Security
Despite the many security measures implemented during access, the cloud infrastructure has security flaws that need an extra layer of protection. Google workspace data is stored in the cloud connected to the enterprise network and accessed by different users. Zero trust security is critical to secure information. Zero trust security assumes that all devices and applications connecting to the data storage are unsafe and must authenticate themselves whenever they access the data. Figure 1 below depicts zero trust security in an enterprise.
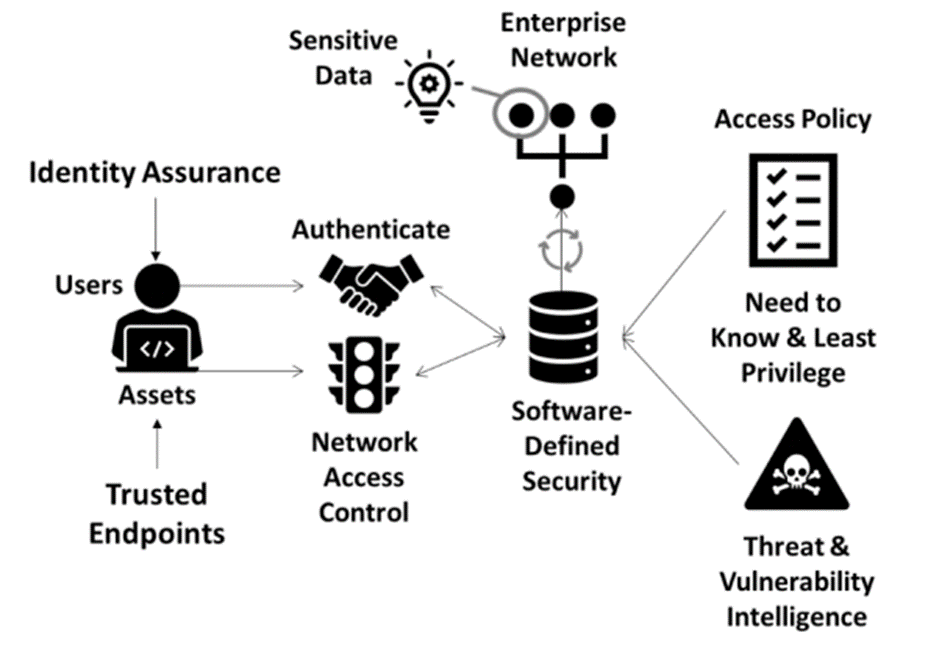
Figure 1: Zero trust security (Schreider, 2019).
From the figure, all access points are treated as insecure. All users have to authenticate to access the data. The access policy is also restricted to a need basis, with the least privilege for all employees, making it hard for anyone to access information that does not support their work. The enterprise network also authenticates itself when accessing secure data. Bio-Human can implement zero trust where Google workspace information is stored in the cloud, and all users are treated as suspects, requiring authentication and authorization to the workspace. The network channel used by BioHuman’s employees is also treated as insecure, and authentication mechanisms are implemented to ensure it is secure every time employees access workspace. The authentication mechanism requires a system that acts as a proxy, checking the security of the user, an individual, or an application, accessing the data. The proxy is between the users and the cloud storage, ensuring all access is authenticated according to predefined policy (Cisco Nederland, 2019). Additionally, all authorized access to the data without passing through the proxy is denied as the system deems such access as insecure, making it hard for rogue attackers to access data even when using legitimate usernames and passwords. Google workspace is accessed by authorized users only using secure networks and devices.
Summary
Google workspace is a cloud collaboration suite of tools that help enterprises communicate with each other irrespective of distance or time. Workspace only requires a connection to the internet. However, cloud-based tools make them vulnerable to hackers, as anyone in the world can access them with the proper credentials. This makes Google workspace security essential for enterprises such as BioHuman as it needs to protect its patient data. Some of the best security measures BioHuman can use include secure cloud access, where the cloud administrator has an identity management system that provides all login credentials to BioHuman employees. Besides, the identity management system needs monitoring to check the user behavior and unauthorized access attempts to the workspace tools. Multifactor authentication is essential to check the authenticity of the user, in which case the user adds another layer of authentication in addition to the username-password combination. Zero trust security has become an essential part of computer systems to ensure all users, both humans and applications, are first authenticated by the system or a proxy before accessing the company’s data. Bio-Human requires measures to protect the sensitive health information it holds, creates, and uses daily.
References
Cisco Nederland. (2019, June 3). How zero trust improves security and the user experience [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-Why_ZjJUhg
Schreider, T. (2019). Building an Effective Cybersecurity Program (2nd ed.). Rothstein Associates.
Soltero, J. (2020, October 6). Introducing Google workspace. Google Cloud. https://cloud.google.com/blog/products/workspace/introducing-google-workspace
Microsoft (2019). What is: Multifactor authentication. https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/topic/what-is-multifactor-authentication-e5e39437-121c-be60-d123-eda06bddf661
Netskope. (n.d.). Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB). https://www.netskope.com/security-defined/what-is-casb Yang, L. L. (2020, December 31). Cloud security explained! Hear from a pro hacker! [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gTPjwkXt20k


