Question 1
Correct!
FEEDBACK: When the price level falls, firms have the incentive to decrease their output and, hence, real GDP. The incentive to decrease output lies in menu costs, money illusion and sticky input prices. As a result, GDP falls.
Question 2
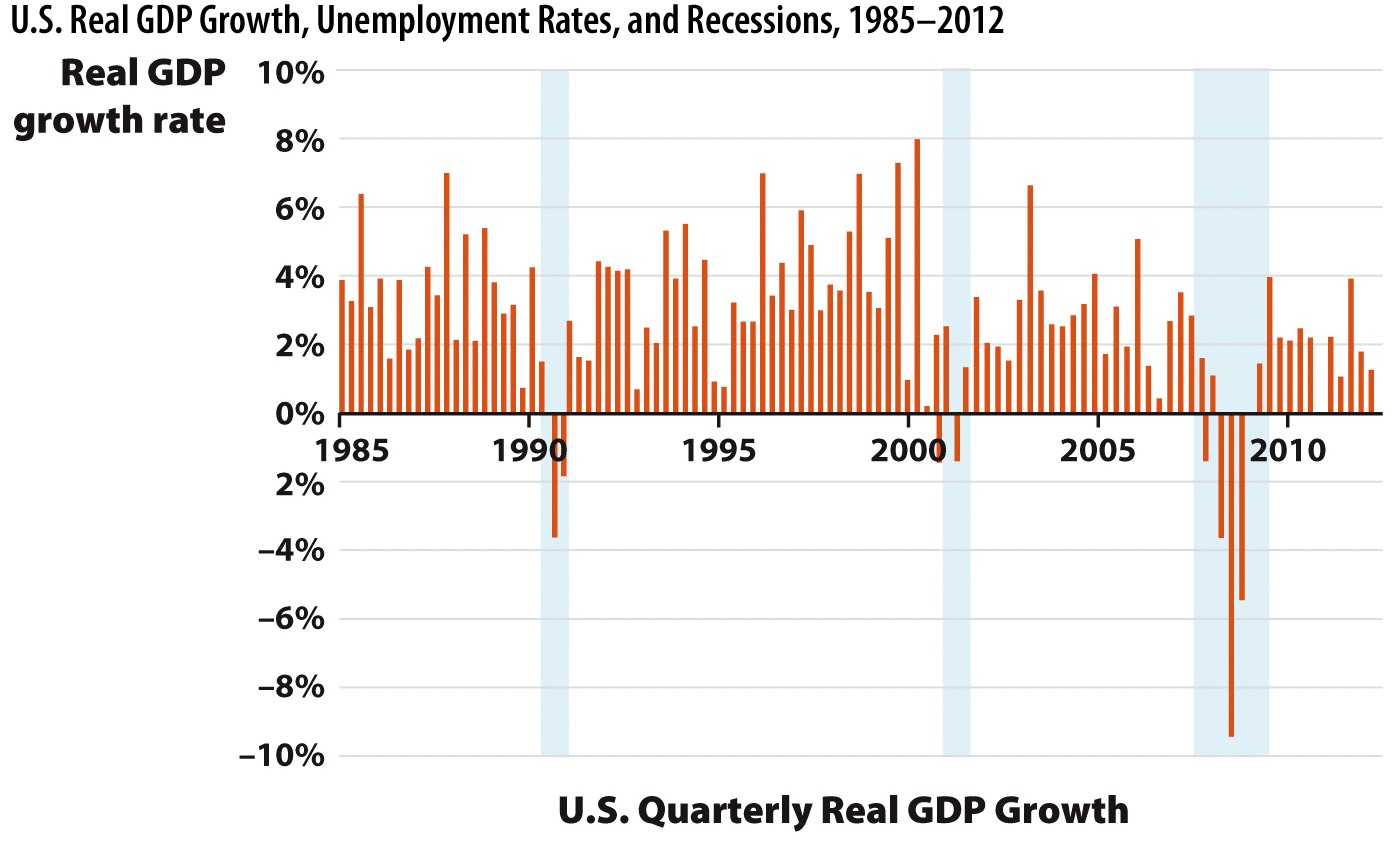
Refer to the figure below. It is apparent that between 1992 and 2000 the U.S. economy went through the _________ phase of the business cycle.
Correct!
FEEDBACK: Changes in real GDP remained positive through each quarter between 1992 and 2000 so we know that the U.S. economy was expanding during this time. In addition, the blue shaded areas indicate a time when the economy is going through a contractionary phase or recession.
Question 3
Correct!
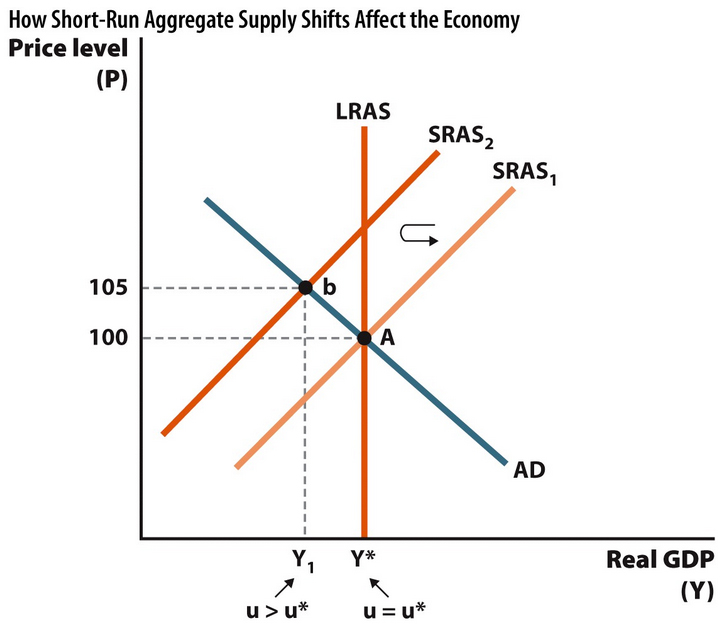
FEEDBACK: Oil is an important input for many firms, and a decrease in oil prices will lower average input prices for those firms. Lower input prices result in a lower cost of production at every price level, so firms are willing to produce more output at every price level, and the short-run aggregate supply curve shifts to the left. The long-run aggregate supply curve does not shift because this is a temporary shock.
Question 4
Correct!
FEEDBACK: Many people own stocks and mutual funds that are tied to the stock market. When the stock prices increase, their wealth increases, and they may be inclined to spend more today. The result is an increase in aggregate demand.
Question 5
Correct!
FEEDBACK: Based on the graph below, after a change in SRAS, the economy returns to long-run equilibrium when the SRAS eventually shifts back to exactly where it was originally. The new graph of long-run equilibrium will be exactly the same, implying no long-run change to the price level. If the LRAS curve shifts, output and the price level both shift in the long run. If the aggregate demand curve shifts, output remains the same in the long run but the price level shifts.
Review the figure below,
FEEDBACK: Based on the graph below, after a change in SRAS, the economy returns to long-run equilibrium when the SRAS eventually shifts back to exactly where it was originally. The new graph of long-run equilibrium will be exactly the same, implying no long-run change to the price level. If the LRAS curve shifts, output and the price level both shift in the long run. If the aggregate demand curve shifts, output remains the same in the long run but the price level shifts.
Review the figure below,
Question 6
Correct!
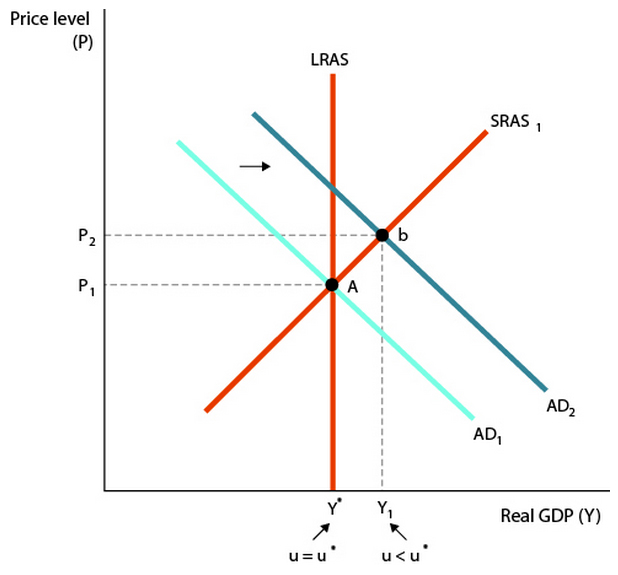
FEEDBACK: Referring to the graph below, in the short run, Real GDP rises, the unemployment rate falls, and the price level rises. In the long run, real GDP goes back to the full-employment level, the unemployment rate returns to the natural rate, and the price level rises further. In the short run, AD curve shifts from AD1 to AD2. Equilibrium will be at point b. In the long run, equilibrium will be at point C
FEEDBACK: Referring to the graph below, in the short run, Real GDP rises, the unemployment rate falls, and the price level rises. In the long run, real GDP goes back to the full-employment level, the unemployment rate returns to the natural rate, and the price level rises further. In the short run, AD curve shifts from AD1 to AD2. Equilibrium will be at point b. In the long run, equilibrium will be at point C
Question 7
Correct!
FEEDBACK: For economy A, high nominal wages are set for five years. Therefore they cannot adjust for five years. The SRAS cannot increase for five years, and the economy cannot get back to long run equilibrium for at least five years. This makes the recession last longer. For economy B, wage contracts are going to change annually with the price level. Since wages can adjust relatively quickly, SRAS will be able to increase more quickly than in economy A. This will end the recession and bring the economy back to a long run equilibrium relatively faster.
Question 8
Correct!
FEEDBACK: The three effects that explain why an increase in the price level causes a decrease in real gross domestic product are the wealth effect, the interest rate effect, and the international trade effect. An increase in the price level of the U.S. raises the price of U.S. goods relative to the price of foreign goods. So, imports are less expensive and exports are more expensive. The net export component of GDP decreases, lowering real GDP.
Question 9
Correct!
FEEDBACK: When the price level in the United States decreases, all else constant, U.S. goods become cheaper relative to foreign goods. This means that people in the United States buy fewer foreign goods, so imports fall. Exports also rise, because other countries will buy more U.S. goods. Since imports are subtracted from net exports, this means that net exports rise. Therefore, a lower price level increases the quantity of aggregate demand. This is the international trade effect, which contributes to the downward slope of aggregate demand. Note that the change in price level does not cause a shift in aggregate demand, but only a change in quantity of aggregate demand, or a movement along the aggregate demand curve.
Question 10
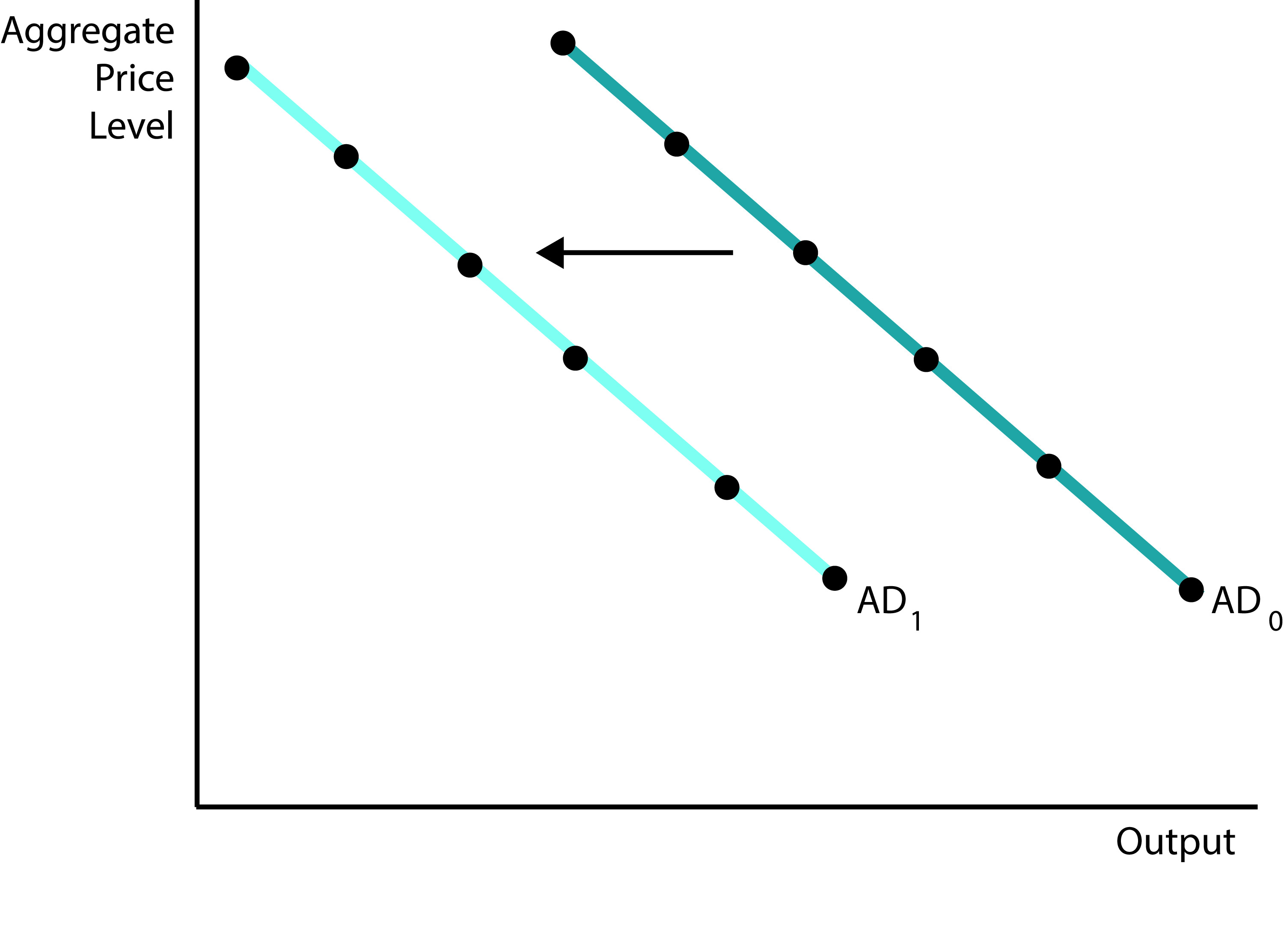
Click to view larger image.The shift in aggregate demand depicted above is due to a(n):
Correct!
FEEDBACK: An increase in income taxes leads to a decrease in disposable income, which leads to a decrease in consumer spending. This will cause aggregate demand to decrease and the aggregate demand curve will shift leftwards. An increase in consumer confidence will lead to increased consumer spending. A decrease in interest rates will lead to an increase in consumer and investment spending. An increase in exports will lead to an increase in consumer spending. These 3 factors will all shift the aggregate demand curve rightwards.
Question 11
Correct!
FEEDBACK: When consumer wealth rises due to an increase in housing prices, aggregate demand will increase. Output and the price level are greater than at full-employment output. In the short run, input prices are sticky and do not change. In the long run, contracts are renegotiated and the short-run aggregate supply curve shifts to the left. The new equilibrium restores the full-employment output level, but also results in a new, higher price level.
Question 12
You work for Dr. Zhang, the autocratic dictator of Zhouland. After taking an economics course, you decide that devaluing your currency (Zhoullars) is the way to increase GDP. Following your advice, Dr. Zhang orders massive increases in the supply of Zhoullars, which reduces the value of Zhoullars in world markets. Use the AD–AS model and assume the economy was in long-run equilibrium before this change. Remember to consider only this change as you determine your answers.
In the short run, the policy will cause the price level to ___________, real GDP to___________, and the unemployment rate to___________.
Correct!
FEEDBACK: The reduction in the value of the Zhoullar means an increase in AD. The value of the dollar (or Zhoullar, in this case) is a shift factor for AD. In this case, a devaluing of the Zhoullar leads to an increase in AD. The new intersection with SRAS will be at a price level above the long-run equilibrium price level, at a level of real GDP above the long-run equilibrium level of real GDP, and at a level of unemployment below its natural rate.
FEEDBACK: The reduction in the value of the Zhoullar means an increase in AD. The value of the dollar (or Zhoullar, in this case) is a shift factor for AD. In this case, a devaluing of the Zhoullar leads to an increase in AD. The new intersection with SRAS will be at a price level above the long-run equilibrium price level, at a level of real GDP above the long-run equilibrium level of real GDP, and at a level of unemployment below its natural rate.
Question 13
Correct!
FEEDBACK: A lower rate of investment is something that would lead to a decrease in the long run aggregate supply. Unfavorable weather in corn-producing states is temporary and would lead to a decrease in short run aggregate supply. Favorable weather is also temporary and will lead to an increase in short run aggregate supply. Advances in technology will lead to an increase in long run aggregate supply, because it will tend to increase productivity for firms and this is something that will be sustained and permanent.