FEEDBACK: The total consumer surplus is the amount of consumer surplus for every individual added together. In this market we have two consumers with a willingness to pay $10 and $9. We subtract the market price from each individual’s willingness to pay in order to find the consumer surplus for that individual. Consumer surplus for Austin is $10 – $6 = $4 and consumer surplus for Erin is $9 – $6 = $3. Total consumer surplus is $4 + $3 = $7.
FEEDBACK: Deadweight loss is the surplus that was present before the tax was introduced but that doesn’t show up in consumer surplus, producer surplus, or government revenue once the tax is in place.
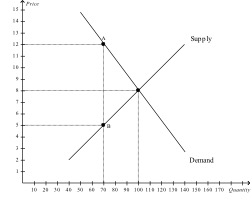
Looking at the following graph, consider a price floor at $5. The deadweight loss from the imposition of this price floor is
FEEDBACK: To compute the amount of the deadweight loss, we need to determine the area of the Triangle that would have been part of consumer or producer surplus without the market distortion. In this case the triangle is represented by the equilibrium (at the intersection of supply and demand), point A, and point B. The area of a triangle is found by taking one-half x the base x the height. The triangle is sitting on its side, so the height of the triangle is 30 (100 – 70) and the base is $7($12 – 7). Hence, the deadweight loss is x 7 x 30 = 105.
Which of the following is not a characteristic of an efficient market?
FEEDBACK: Markets are efficient (meaning that social welfare is maximized) at the equilibrium point. At the equilibrium point, quantity supplied will equal quantity demanded and deadweight loss will equal zero. This is where the maximum amount of total surplus (consumer surplus plus producer surplus) is achieved.
FEEDBACK: Communities lose jobs when a binding minimum wage is enacted because labor becomes more expensive and demand for labor falls. In addition, if a company can cut labor costs by moving its business to areas that pay lower wages, it will. If the nearby city enacts the same minimum wage, firms will not have the option to save money by relocating to an area with lower equilibrium wages, and the suburb will not lose jobs because firms shift locations.
FEEDBACK: The quantity of chocolate demanded will decrease, since the artificially high price will cause consumers to seek out cheaper substitutes for chocolate. According to the law of demand, as price rises for a good, the quantity demanded falls.
FEEDBACK: The quantity of chocolate supplied will increase, since the high price gives producers an incentive to shift resources toward chocolate production. According to the law of supply, as price rises for a good, the quantity supplied rises.